Architecture Overview
DALL·E 2 consists of three required components:
- CLIP Encoder: maps text and images into the same embedding space, enabling direct comparison between them.
- Prior: transforms text embeddings into image embeddings, acting as a bridge between CLIP's text encoder and the diffusion decoder.
- Decoder: generates final images conditioned on the image embeddings.
- Upsampler (Optional): increases the image resolutions.
Simply stated, the goal of DALL·E 2 is to generate images that look like an input text description. The CLIP encoder encodes the text description into a high-dimensional vector, the text embedding. The prior tells the model how that text embedding should look in the form of an image embedding, filling the gap between language and vision. And the decoder uses the output of the prior – containing information about how the image should look – to generate the final image.
CLIP Encoder
The CLIP encoder converts text and images into vectors in the same embedding space, enabling direct comparison between them. For DALL·E 2, the text caption is fed into CLIP's text encoder to produce a high-dimensional text embedding that captures the meaning of the caption. This embedding forms the foundation on which the prior and decoder build the final image.
Prior
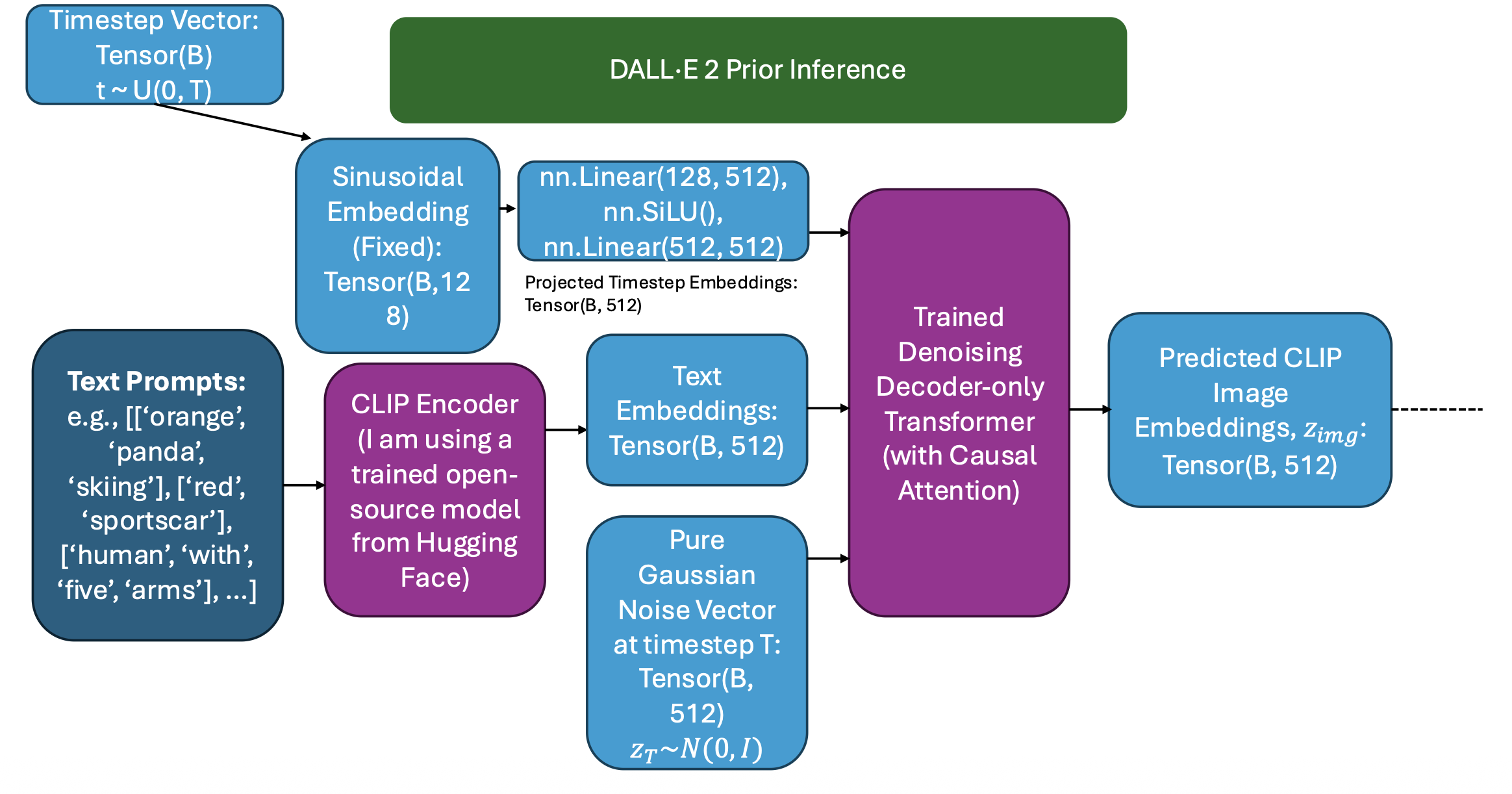
The prior's objective is to predict the conditional probability distribution between the CLIP text and image embeddings, \(z_{img} \sim P(z_{img} | z_{txt})\).
The prior is a transformer model that takes the CLIP text embedding as the input and predicts the corresponding CLIP image embedding. It learns from many text-image pairs what an image embedding should look like for a given caption and predicts that embedding for the decoder to use.
First, a timestep is uniform randomly sampled as an integer. An MLP projects this 128-dimensional embedding into the transformer's model dimension. The other two inputs to the transformer are the CLIP text embedding (B, 512) and a Gaussian noise tensor (B, 512).
A decoder-only transformer with causal attention (a transformer that prevents tokens from seeing future tokens) predicts the CLIP image embeddings, which tell the decoder what the images in the batch should look like.
Decoder
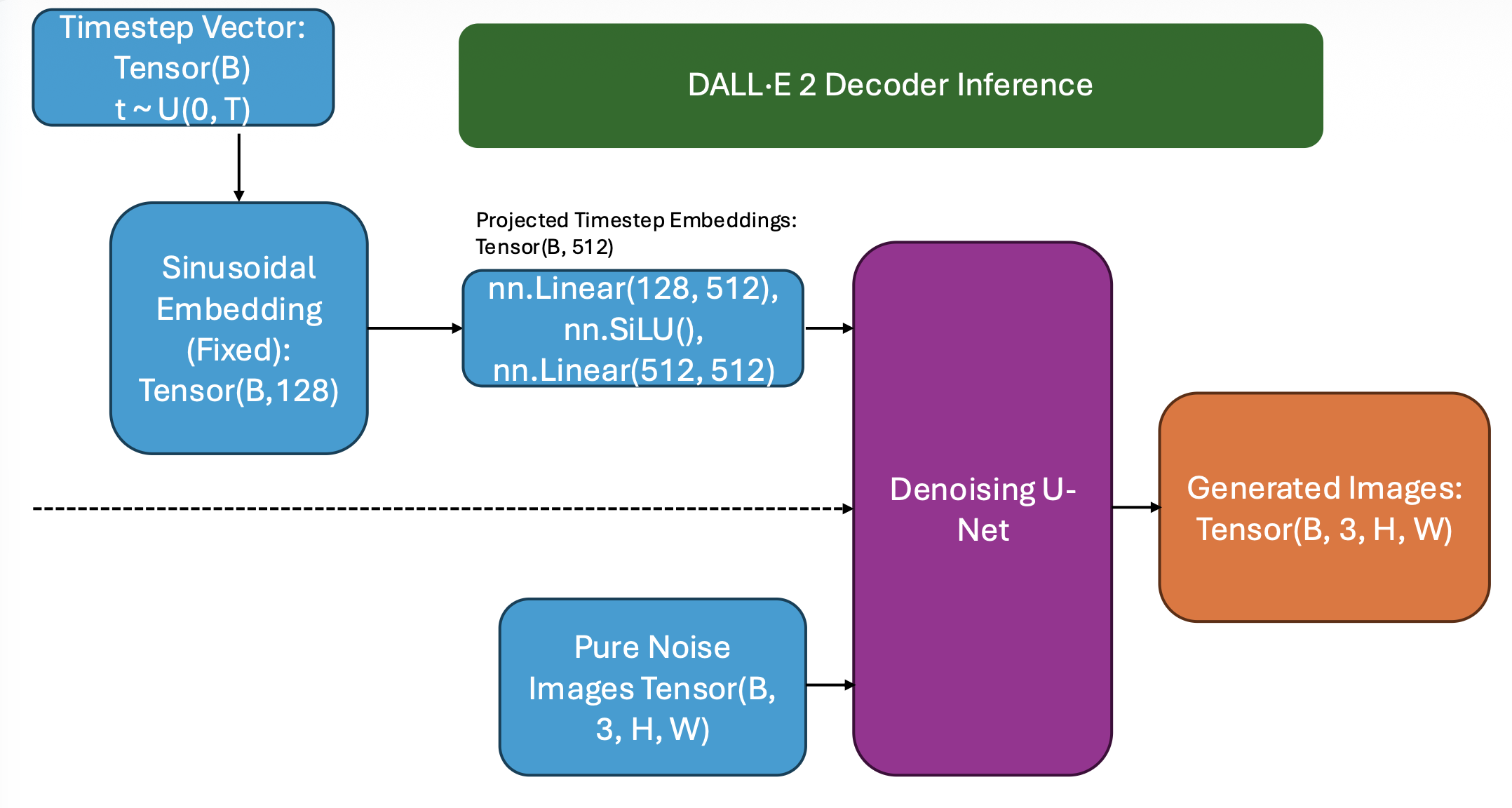
The decoder's objective is to predict \(x_0 \sim P(x_0 | z_{img})\), where \(x_{0}\) represents the final denoised image.
The decoder is a diffusion-powered U-Net. The sinusoidally embedded and MLP-projected timestep, the CLIP image embeddings (the prior's output), and a Gaussian noise tensor of shape (B, 3, H, W) are fed into the U-Net. At each timestep, the U-Net removes a portion of the noise – guided by the CLIP image embedding – following the denoising process learned during diffusion training.
Upsampler
The upsampler is a super-resolution diffusion model that increases the decoder's low-resolution image to a higher resolution. It receives a noised version of the decoder's output along with the CLIP image embedding, and denoises the image step-by-step to add detail, texture, and sharpness. This produces a final, high-resolution image conditioned by the original text caption.